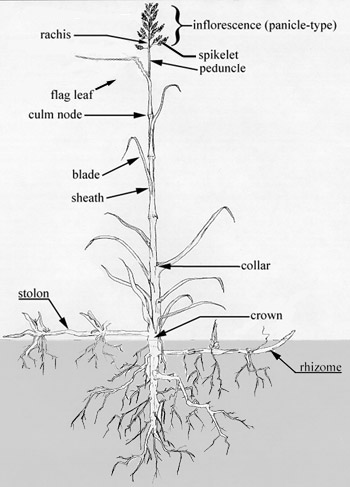
The zone of division the zone of elongation and the zone of maturation. A rhizome is a segmented subterranean modified stem arising from an adventitious bud in the crown zone.
Rhizomes And Stolons Forage Information System Oregon State University
Difference Between Rhizomes And Stolons.
. They are elongated branches of the existing stem of the plant. These longer stolons called runners include internodes sections between nodes. Stolons and rhizomes are modified stems for vegetative reproduction.
Describe how plant cells grow. The production of stolons can be a desirable. The main difference between them however is that while the stolons almost always develop above the ground and very close to it the rhizomes are always underground stems also horizontally growing that produce roots and shoots in their.
Buds form at different parts along the structure not necessarily at the top. The main difference between them however is that while the stolons develop almost always above the ground and very close to the ground the rhizomes are always underground stems also of horizontal. Explain how taproot systems and fibrous root systems differ.
They are crucial in vegetative. Plant cells go through different phases. Describe how plant cells grow.
Stolons Stolons are longer and appear depressed. The seeded cultivars La Paloma and Yukon had lower stolon and rhizome density than the vegetative cultivars with Patriot producing more vegetative stems than Tifway Figures 1 and 2. Results of this trial showed that there were significant differences in stolon and rhizome development between bermudagrass cultivars throughout the study period.
These results collectively revealed that stolons and rhizomes of bermudagrass have significant differences at the proteome level and light might play important regulatory roles in. To the horticulturist the terms bulbs tubers rhizomes and corms all have distinct meanings. Examples of rhizomes are Bearded Iris Canna Lilies and Calla Lilies.
Horizontal shoots that grow along the surface for asexual reproduction. Difference Between Corms and Bulbs. Identify and explain the difference between vegetative and reproductive tillers Compare and contrast rhizomes and stolons Identify traits that distinguish a sod-forming grass from a.
When the supply of sugars from the leaves exceeds the demand for new leaf development and growth certain grass species may develop a rhizome. The following factors summarize the main differences between stolons and rhizomes. Describe the differences in structure and function of the two types of sclerenchyma cells.
Rhizomes branch out and each new portion develops roots and a shoot of its own. Instead they loosely call all of these swollen underground plant parts bulbs. Explain the differences between stolons and rhizomes.
A popular plant known for its stolons is the strawberry Fragaria. Distinguish between parenchyma and collenchyma cells with regards to structure and function. Describe the differences in structure and function of the 2 types of sclerenchyma cells.
Distinguish between parenchyma and collenchyma cells with regards to structure and function. Rhizomes Rhizomes are fleshy but shorter than stolons. The key difference between rhizome and stolon is that rhizome is the root-like main stem that grows underground while stolon is a stem sprouted from the existing stem that runs horizontally just below the soil surface to form a new plant and connect with the mother plant.
Its root has points in direct correlation to the length that continues the cycle to make new plants. Explain the importance of tracheids and vessel elements to plants. Stolons Unlike rhizomes stolons are usually not fleshy and appear slender.
Explain the differences between stolons and rhizomes. Describe the differences in structure and function of the 2 types of sclerenchyma cells. A stolon sprouts from an existing stem.
A rhizome is the stem of a plant. The rhizomes and stolons perform functions very similar in plants since both are cases of asexual vegetative reproduction. Explain the differences between stolons and rhizomes.
Describe how plant cells grow. Stolon roots grow horizontally above the ground while rhizomes grow horizontally just below the surface soil. Rhizomes Rhizomes are usually thicker fatter and bulkier than stolons.
Rhizomes are stem-like structures that grow horizontally across the ground forming roots from the bottom while sending shoots upward. Rhizomes are stems that grow sideways rather than up running along the surface of the soil or just below it. Rhizomes store nutrients for newly growing plants.
Rhizomes and stolons are special structures of plants. Both gardeners and plant companies have a tendency to call any roundish knobby plant root a bulb but there are distinctions between true bulbs corms and rhizomes. A rhizome is a root-like stem which is the main stem that can grow horizontally or other directions underground.
Distinguish between parenchyma and collenchyma cells with regards to structure and function. Plants that use rhizomes for food storage have fatter more bulblike rhizomes covered with a dry base of leaves. Horizontal shoot located below the surface - stolons.
But when gardeners are speaking casually they often fail to make a distinction between them. While stolons grow above the ground rhizomes grow beneath the ground. Stolons and rhizomes maintain the genotypes of.
Describe how plant cells grow. The rhizomes and stolons perform very similar functions in plants since both are cases of asexual vegetative reproduction. A stolon is a horizontal and creeping plant stem which is famous for its other name as a runner.
While they are usually planted similarly there can be important differences.

Differences And Similarities Between Stolons And Rhizomes Youtube
What Is The Difference Between Stolon And Rhizome Pediaa Com

0 Comments